Do you know LED display Point-by-point correction technology ?
News

Do you know LED display Point-by-point correction technology ?
1.What is Point-by-Point Correction
Point-by-point correction is a technology used to improve the brightness and color uniformity and color fidelity of LED display, i.e., by collecting the brightness (and chromaticity) data of each pixel (or each base color sub-pixel) area on the LED video wall, giving the correction coefficients or correction coefficient matrices of each base color sub-pixel or each pixel, and feeding them to the control system of the rental led display, which will apply the correction coefficients to By applying the correction coefficients, the control system realizes the differential drive for each pixel (or each base color sub-pixel), so that the picture of the LED display screen is pure and delicate and the colors are truly reproduced.
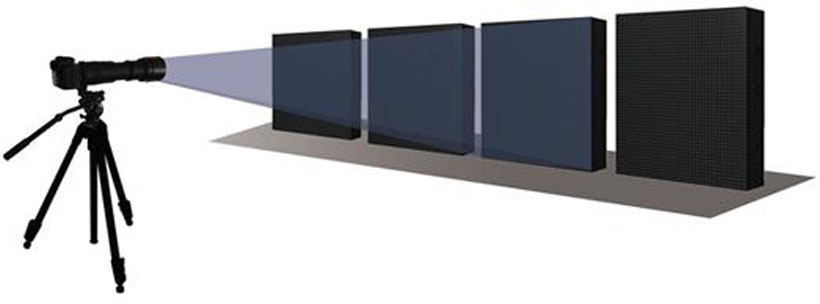
2.The basic principle of point-by-point calibration
Point-by-point calibration requires the cooperation of “control system” and “point-by-point calibration system”, in which the point-by-point calibration system is responsible for “generating correction coefficients” and the control system is responsible for “applying correction coefficients”. The point-by-point correction system is responsible for “generating correction coefficients” and the LED display control system is responsible for “applying correction coefficients”, both of which are indispensable.
Calibration system through a professional camera on the LED display imaging, access to the brightness and color of each LED light, for each pixel to generate a unique set of correction coefficients, and then the correction coefficients sent to the control system to save and solidify. When the control system is running, it completes high-speed multiplication operation with the correction coefficients for the image content of each pixel, thus completing the point-by-point correction.
Point-by-point correction can be divided into point-by-point brightness correction and point-by-point chromaticity correction.
Basic principles of point-by-point luminance correction and point-by-point chrominance correction
Point-by-point brightness correction
Usually the brightness correction is the correction of LED luminous intensity, LED display is composed of pixel array, each pixel has red, green and blue three-color LED composition, the brightness of the LED is controlled by the control system's pulse width, the different brightness of the red, green and blue LEDs combined into a variety of brightness and color that we need. In order to achieve better brightness uniformity, after setting the target, for the LED lights whose brightness is higher than the target value, the control pulse width can be appropriately compressed to reduce its brightness and reach the target value.
Point-by-point Chromaticity Correction
Point-by-point chromaticity correction is based on the basic principle of chromaticity compensation, which compensates for the base color by two other base colors, and achieves color adjustment by mixing colors. For example, if the red light of a pixel is too red (i.e., the wavelength is too long), we can make the pixel red light, so that the green and blue lights should not be bright with a little bit of light (the specific green and blue with how much light is the result of image acquisition, image recognition, image processing and arithmetic). In this way, after the color mixing, the human eye will feel the red light is not so red.

The advantages of point-by-point chromaticity correction over point-by-point luminance correction are as follows:
1. point-by-point chromaticity correction can achieve higher luminance uniformity (point-by-point luminance correction cannot solve the problem of chromaticity non-uniformity);
2. in point-by-point chromaticity correction can obtain smaller brightness sacrifice. For the general display, point-by-point brightness correction needs to sacrifice about 15% to 20% of the brightness, while point-by-point chromaticity correction only needs to sacrifice 5% to 8% of the brightness. This is for those who have been used for many years, the brightness has been attenuated to a relatively low display, this advantage is particularly critical.
3. LED display why need to do the correction?
Display “flower” problem
Because even between the same batch of LED lights, there will still be about 10% brightness deviation, coupled with the differences in the driver IC, so the display is inherently flowery.
Problem of splicing bright and dark lines
As the current sheet metal processing accuracy has been unable to meet the requirements of the splicing accuracy of small-pitch LED products, so the cabinet and the module will inevitably produce bright and dark lines between.
Mosaic phenomenon
Due to the light distortion or two batches of mixed use and other reasons that lead to the LED display there are obvious light and dark blocks.
Color distortion
As the color gamut of LED display is relatively wide, so the screen color may be different from the LCD, that is, we call “color distortion”. Through the chromaticity correction technology, the color gamut space can be converted to maximize the restoration of the true display effect.
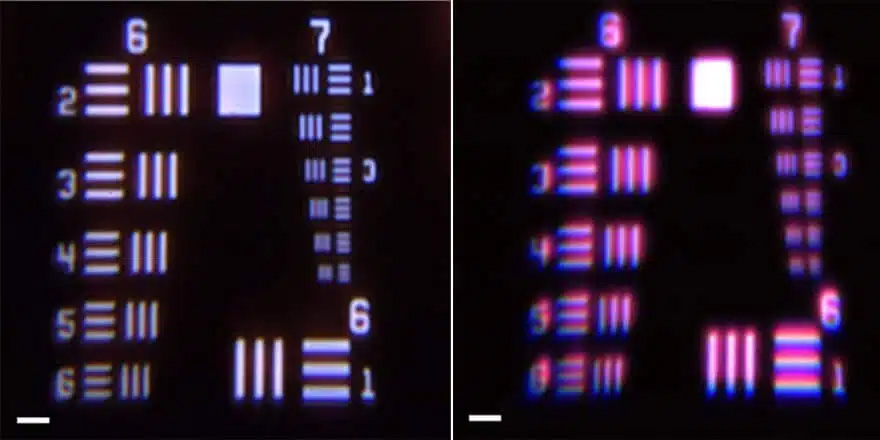
Specific applications of point-by-point calibration system
Single-LED cabinet point-by-point calibration, Cabinet-by-Cabinet calibration in the production line, to ensure that each panel from the factory to achieve a high degree of uniformity;
On-site large-screen point-by-point calibration, on-site calibration at the large-screen display site by selecting a suitable viewing location to ensure that the display reaches a high degree of uniformity in the field observation position;
Why do we need production line calibration technology?
First of all, due to the differences between the LED and the driver IC, make the display born very flower, especially small pitch, because its current are lower than 5 mA, so the difference will be even greater, if all the whole screen calibration, for the factory, it will be a time-consuming and laborious work;
Secondly, for leasing users, multiple batches of box mixing, the use of different time limits of the box mixing occurs from time to time, and the need for any splicing. Both of these needs require LED display production line calibration.

5.The two most common misconceptions about point-by-point calibration
Myth: only the old screen needs calibration, the new screen does not need.
Positive solution: due to the differences between the LED and the driver IC, making the LED display born very flowery, especially the small pitch, because its current are less than 5 mA, so the difference will be even greater. So it is necessary for the display to be calibrated at the factory.
Myth: Correction is damaging the display and cannot restore the original brightness.
Positive solution:
1. In order to achieve good uniformity, the brightness of the light needs to be too bright down “pressure”, for the new screen, only need to pressure 5% ~ 10% can be;
2. Correction is only “pressure” the brightness of the screen, and did not “sacrifice” the brightness of the screen; for example, a screen brightness of 5000 cd, assuming that the choice of pressure 10% to correct the words, after correction of the brightness of 5000 cd * 0.9 = 4500; After correction, if you cancel the correction, the brightness will be restored to 5000cd immediately;
That is to say, for this screen, whether it is calibrated 1 time, or calibrated 2 times, or calibrated 100 times, the brightness is still 4500cd after calibration, if you cancel the calibration, it will be restored to “5000cd” immediately.
 18027665203
18027665203